In the previous blog post, we introduced the Orange fairness addon along with the Dataset Bias and As Fairness widgets. We also demonstrated how to use them to detect bias in a dataset and visualized the results for a better understanding. In this blog, we will introduce the Reweighing widget, which we can use to mitigate bias in a dataset, resulting in fairer machine learning models learning from it.
Reweighing:
The Reweighing widget offers a solution to mitigate bias in datasets by assigning weights to individual instances. These weights are determined using the Reweighing algorithm. Essentially, the algorithm gives higher weights to underrepresented pairs of protected attributes and classes and reduces weights for overrepresented ones. This strategy encourages the model to prioritize learning from underrepresented groups while de-emphasizing overrepresented groups. In Orange, we can use the Reweighing widget in two ways:
Reweighing a dataset: The widget can be used to reweigh a dataset, which we can then use to train a model. Simply connect your dataset to the widget, and the output will be a dataset with appropriately weighted instances.
Reweighing as a preprocessor: The widget can function as a preprocessor for a specific model. By connecting the Reweighing widget directly to your chosen model, the dataset is automatically reweighed prior to the training phase.
Orange use case
Now that we have grasped how the Reweighing widget functions and its applications, let us explore a real-world example of using it to assign weights to data.
For this illustration, we will use the Compas dataset. The COMPAS dataset, obtained from ProPublica, contains 7,214 cases with 52 attributes, of which 33 are categorical and 20 are numerical. The most frequently used protected attributes are race and gender. The main goal with this dataset is to predict the likelihood of a convict being re-arrested.
Contrary to the example in the previous blog, we will not use the As Fairness widget to select fairness attributes. This is because datasets with a fairness tag come with default fairness attributes. Specifically, for the Compas dataset, “race” is identified as the protected attribute, with “Caucasian” set as the privileged, protected attribute value.
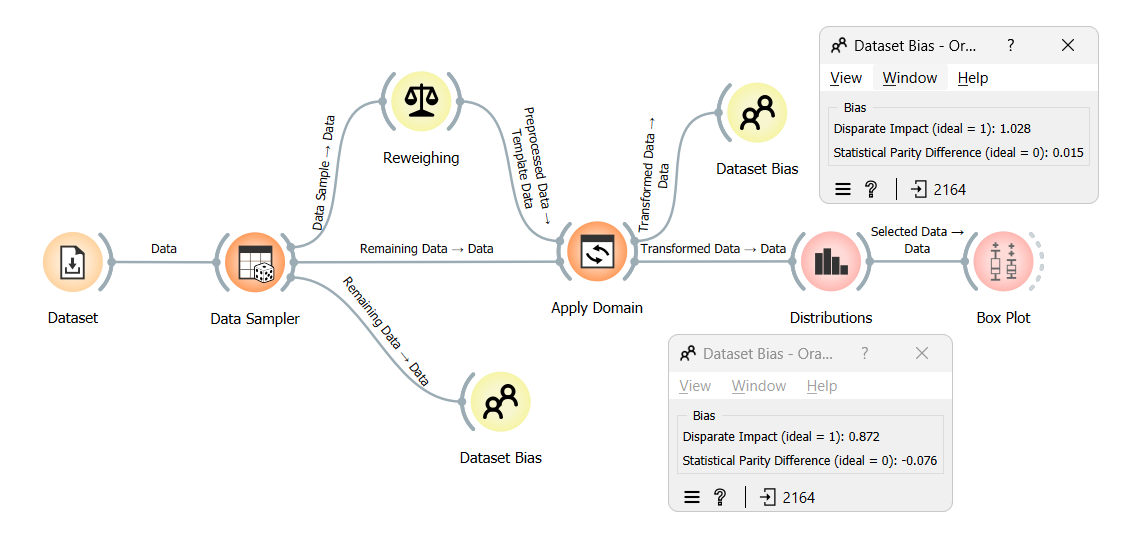
From the results, we can see that after reweighing the dataset, bias decreased substantially, nearing zero. Let us start by highlighting instances with lower or higher weights in the distribution widget to understand how the reweighing process assigned weights. Following this, we will analyze which combinations of protected attributes and classes were allocated these distinct weights.
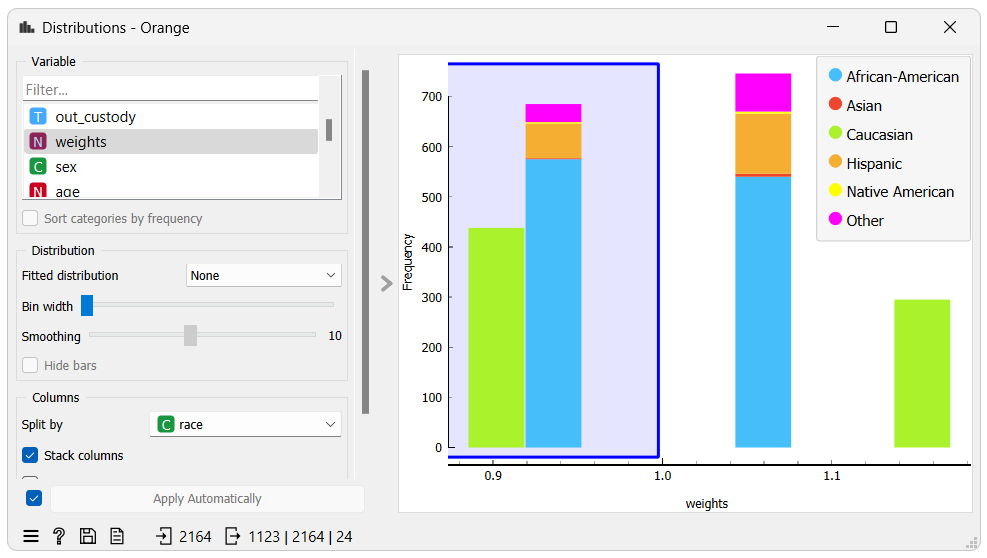
In the distributions widget we selected instances which have been assigned a weight lower than 1.0. Let’s inspect the selected instances using a box plot widget.
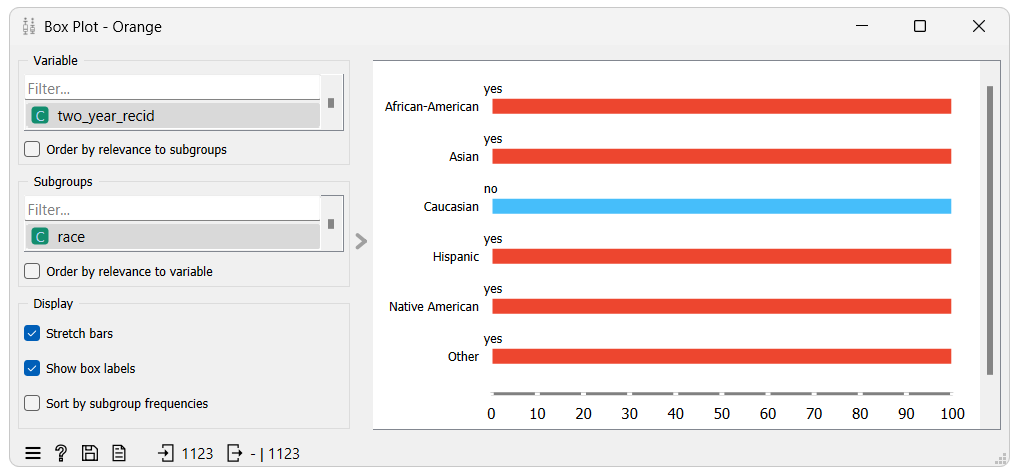
The box plot widget reveals that lower weights were given to instances of unprivileged groups with unfavorable class values and privileged groups with favorable class values. The opposite is true for the higher weights. The results show that the reweighing algorithm assigned weights to the instances in a way that will encourage the model to prioritize learning from underrepresented groups while de-emphasizing overrepresented groups.
In the context of the dataset, the reweighing algorithm recognized that there were more instances with the race “Caucasian” and the favorable class value “no” than any other race and the opposite for the unfavorable class value “yes”. Because of this, it assigned the instances with the race “Caucasian” and the class value “no” a lower weight, encouraging the model to focus less on these instances, while giving the instances of other races with the class value “no” a higher weight, encouraging the model to focus more on these instances. The same is true for the class value “yes” but in the opposite direction.
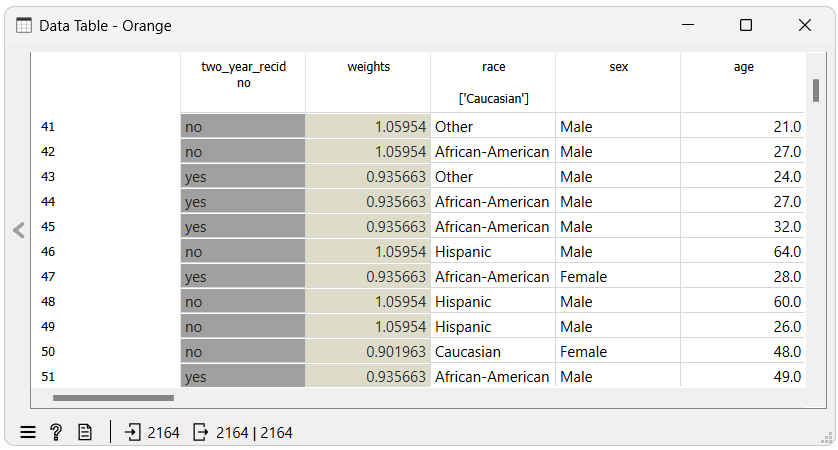
Another way to see the effects of using the Reweighing widget on a dataset is to use a Data Table widget, where we can see that a new meta attribute called weights has been added to the dataset. This attribute contains the weights assigned to each instance.