Feature scoring and ranking can help in understanding the data in supervised settings. Orange includes a number of standard feature scoring procedures one can access in the Rank widget. Moreover, a number of modeling techniques, like linear or logistic regression, can rank features explicitly through assignment of weights. Trained models like random forests have their own methods for feature scoring. Models inferred by these modeling techniques depend on their parameters, like type and level of regularization for logistic regression. Same holds for feature weight: any change of parameters of the modeling techniques would change the resulting feature scores.
It would thus be great if we could observe these changes and compare feature ranking provided by various machine learning methods. For this purpose, the Rank widget recently got a new input channel called scorer. We can attach any learner that can provide feature scores to the input of Rank, and then observe the ranking in the Rank table.
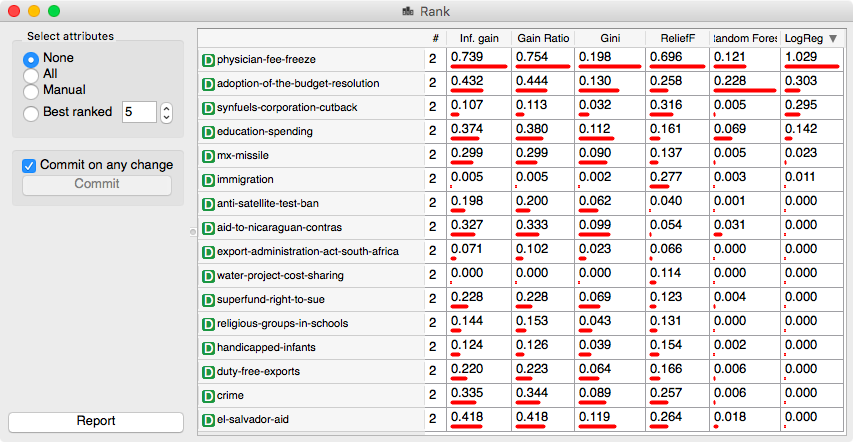
Say, for the famous voting data set (File widget, Browse documentation data sets), the last two feature score columns were obtained by random forest and logistic regression with L1 regularization (C=0.1). Try changing the regularization parameter and type to see changes in feature scores.
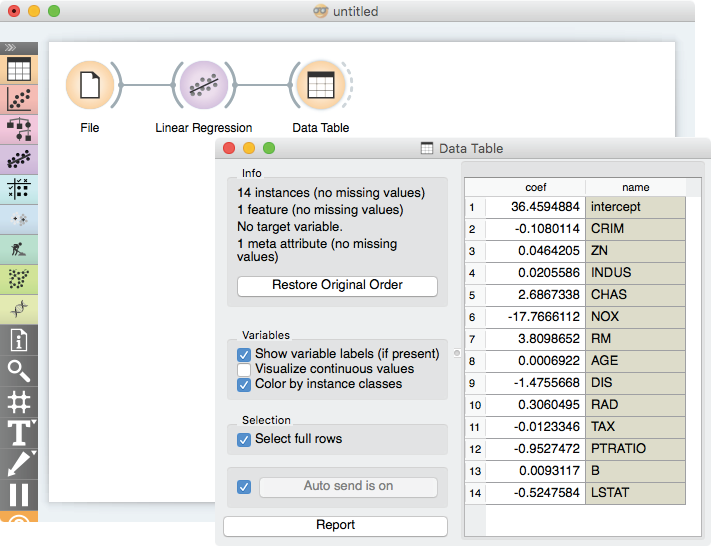
Feature weights for logistic and linear regression correspond to the absolute value of coefficients of their linear models. To observe their untransformed values in the table, these widgets now also output a data table with feature weights. (At the time of the writing of this blog, this feature has been implemented for linear regression; other classifiers and regressors that can estimate feature weights will be updated soon).